|

Argentina
Background:
Following independence from Spain in 1816, Argentina experienced periods
of internal political conflict between conservatives and liberals and
between civilian and military factions. After World War II, a long period of
Peronist authoritarian rule and interference in subsequent governments was
followed by a military junta that took power in 1976. Democracy returned in
1983, and numerous elections since then have underscored Argentina's progress
in democratic consolidation.
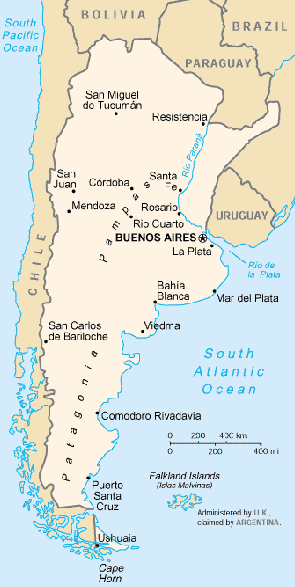
Location:
Southern South America, bordering the South Atlantic Ocean, between
Chile
and Uruguay
Area: Total: 2,766,890 sq km land: 2,736,690 sq km water:
30,200 sq km
Area - comparative: Slightly less than three-tenths the
size of the US
Land boundaries: Total: 9,665 km border countries:
Bolivia 832 km, Brazil
1,224 km, Chile 5,150 km, Paraguay 1,880 km,
Uruguay 579 km
Coastline: 4,989 km
Climate and Terrain:
Climate: Mostly temperate; arid in southeast; subantarctic in southwest
Terrain: Rich plains of the Pampas in northern half, flat to rolling
plateau of
Patagonia in south, rugged Andes along western border
Elevation extremes: Lowest point: Salinas Chicas -40 m (located on
Peninsula
Valdes) highest point: Cerro Aconcagua 6,960 m
Natural
resources: Fertile plains of the Pampas, lead, zinc, tin, copper,
iron
ore, manganese, petroleum, uranium
People:
Population: 37,812,817.
Ethnic groups: White (mostly Spanish and
Italian) 97%, mestizo, Amerindian, or
other nonwhite groups 3%.
Religions: Nominally Roman Catholic 92% (less than 20% practicing),
Protestant
2%, Jewish 2%, other 4%.
Languages: Spanish (official),
English, Italian, German, French.
Government:
Government type: Republic.
Capital: Buenos Aires.
Independence: 9
July 1816 (from Spain).
Economy overview:
Argentina benefits from rich natural resources, a highly literate
population,
an export-oriented agricultural sector, and a diversified
industrial base.
However, when President Carlos MENEM took office in
1989, the country had piled
up huge external debts, inflation had reached
200% per month, and output was
plummeting. To combat the economic crisis,
the government embarked on a path of
trade liberalization, deregulation,
and privatization. In 1991, it implemented
radical monetary reforms that
pegged the peso to the US dollar and limited the
growth in the monetary
base by law to the growth in reserves. Inflation fell
sharply in
subsequent years. I At the start of 2002, newly elected president
Eduardo
Duhalde met
with IMF officials to secure an additional $20 billion loan,
but immediate
action seemed unlikely. The peso's peg to the dollar was
abandoned in January
2002, and the peso was floated from the dollar in
February; inflation picked up
rapidly.
GDP - composition by
sector: Agriculture: 6% industry: 28% services:
66%.
Statistics:
Telephones - main lines in use: 7.5 million.
Telephones - mobile
cellular: 3 million.
Radio broadcast stations: AM 260.
Radios: 24.3 million.
Television broadcast stations: 42.
Televisions: 7.95 million.
Internet users: 3.88 million.
Railways: Total: 33,744 km.
Highways: Total: 215,434
km.
Airports: 1,369.
Return to Visiting Locations
|

