|
Morocco
Background:
Morocco's long struggle for independence from France ended in 1956. The
internationalized city of Tangier was turned over to the new country that same
year. Morocco virtually annexed Western Sahara during the late 1970s, but final
resolution on the status of the territory remains unresolved. Gradual political
reforms in the 1990s resulted in the establishment of a bicameral legislature
in 1997.
Location:
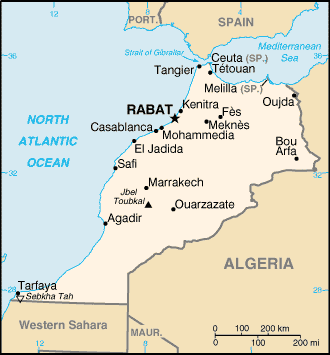
Northern Africa, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea,
between Algeria and Western Sahara.
Area: Total: 446,550 sq km, land: 446,300 sq km, water: 250 sq km.
Area - comparative: Slightly larger than California.
Land boundaries: Total: 2,017.9 km, border countries: Algeria 1,559 km,
Western Sahara 443 km, Spain (Ceuta) 6.3 km, Spain (Melilla) 9.6 km.
Coastline: 1,835 km.
Climate and Terrain:
Climate: Mediterranean, becoming more extreme in the interior.
Terrain: Northern coast and interior are mountainous with large areas of
bordering plateaus, intermontane valleys, and rich coastal. plains
Elevation extremes: Lowest point: Sebkha Tah -55 m, highest point: Jbel
Toubkal 4,165 m.
Natural resources: Phosphates, iron ore, manganese, lead, zinc, fish, salt.
People:
Population: 31,167,783.
Ethnic groups: Arab-Berber 99.1%, other 0.7%, Jewish 0.2%.
Religions: Muslim 98.7%, Christian 1.1%, Jewish 0.2%.
Languages: Arabic (official), Berber dialects, French often the language of
business, government, and diplomacy.
Government:
Government type: Constitutional monarchy.
Capital: Rabat.
Independence: 2 March 1956 (from France).
Economy overview:
Morocco faces the problems typical of developing countries - restraining
government spending, reducing constraints on private activity and foreign
trade, and achieving sustainable economic growth. Following structural
adjustment programs supported by the IMF, World Bank, and the Paris Club, the
dirham is now fully convertible for current account transactions, and reforms
of the financial sector have been implemented. Droughts depressed activity in
the key agricultural sector and contributed to a stagnant economy in 1999 and
2000. During that time, however, Morocco reported large foreign exchange
inflows from the sale of a mobile telephone license and partial privatization
of the state-owned telecommunications company. Favorable rainfall in 2001 led
to a growth of 5%. Formidable long-term challenges include: servicing the
external debt; preparing the economy for freer trade with the EU; and improving
education and attracting foreign investment to boost living standards and job
prospects for Morocco's youth.
GDP - composition by sector: Agriculture: 15%, industry: 33%, services: 52%.
Statistics:
Telephones - main lines in use: 1.391 million.
Telephones - mobile cellular: 116,645.
Radio broadcast stations: AM 27, FM 25.
Radios: 6.64 million.
Television broadcast stations: 35.
Televisions: 3.1 million.
Internet users: 220,000.
Railways: Total: 1,907 km.
Highways: Total: 57,847 km, paved: 30,254 km, unpaved: 27,593 km.
Airports: 67.
with paved runways: 26,
with unpaved runways: 41,
Heliports: 1.
Return to Visiting Locations
|