|

Mozambique
Background:
Almost five centuries as a Portuguese colony came to a close with independence
in 1975. Large-scale emigration by whites, economic dependence on South Africa,
a severe drought, and a prolonged civil war hindered the country's development.
The ruling party formally abandoned Marxism in 1989, and a new constitution the
following year provided for multiparty elections and a free market economy. A
UN-negotiated peace agreement with rebel forces ended the fighting in 1992.
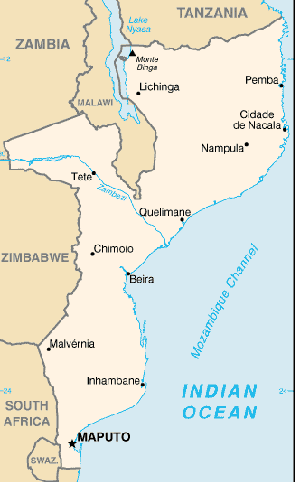
Location:
Southern Africa, bordering the Mozambique Channel, between South Africa and
Tanzania.
Area: Total: 801,590 sq km, water: 17,500 sq km, land: 784,090 sq km.
Area - comparative: Slightly less than twice the size of California.
Land boundaries: Total: 4,571 km, border countries: Malawi 1,569 km, South
Africa 491 km, Swaziland 105 km, Tanzania 756 km, Zambia 419 km, Zimbabwe 1,231
km.
Coastline: 2,470 km.
Climate and Terrain:
Climate: Tropical to subtropical.
Terrain: Mostly coastal lowlands, uplands in center, high plateaus in
northwest, mountains in west.
Elevation extremes: Lowest point: Indian Ocean 0 m, highest point: Monte Binga
2,436 m.
Natural resources: Coal, titanium, natural gas, hydropower, tantalum, graphite.
People:
Population: 19,607,519.
Ethnic groups: Indigenous tribal groups 99.66% (Shangaan, Chokwe, Manyika,
Sena, Makua, and others), Europeans 0.06%, Euro-Africans 0.2%, Indians 0.08%.
Religions: Indigenous beliefs 50%, Christian 30%, Muslim 20%.
Languages: Portuguese (official), indigenous dialects.
Government:
Government type: Republic.
Capital: Maputo.
Independence: 25 June 1975 (from Portugal).
Economy overview:
At independence in 1975, Mozambique was one of the world's poorest countries.
Socialist mismanagement and a brutal civil war from 1977-92 exacerbated the
situation. In 1988, the government embarked on a series of dramatic
macroeconomic reforms designed to stabilize the economy and reduce government
participation. These steps combined with the political stability that has
prevailed since the 1994 multi-party elections have led to dramatic
improvements in the country's growth rate fueled by foreign and domestic
investments and donor assistance. Inflation was brought to single digits during
the same period, although it has returned to double digits in 2000 and 2001.
Foreign exchange rates have remained relatively stable. Fiscal reforms,
including the introduction of a value-added tax and reform of the customs
service, have improved the government's revenue collection abilities. I
Statistics:
Telephones - main lines in use: 90,000.
Telephones - mobile cellular: 100,000.
Radio broadcast stations: AM 13, FM 17, shortwave 11.
Radios: 730,000.
Television broadcast stations: 1.
Televisions: 67,600.
Internet users: 22,500.
Railways: Total: 3,131 km.
Highways: Total: 30,400 km, paved: 5,685 km, unpaved: 24,715 km.
Airports: 166, with paved runways: 22, with unpaved runways: 144.
Return to Visiting Locations
|

