|
South Sudan
Background:
When Sudan gained its independence in 1956, it was with the understanding that
the southerners would be able to participate fully in the political system.
When the Arab Khartoum government reneged on its promises, a mutiny began that
led to two prolonged periods of conflict (1955-1972 and 1983-2005) in which
perhaps 2.5 million people died - mostly civilians - due to starvation and
drought. Ongoing peace talks finally resulted in a Comprehensive Peace
Agreement, signed in January 2005. As part of this agreement the south was
granted a six-year period of autonomy to be followed by a referendum on final
status. The result of this referendum, held in January 2011, was a vote of 98%
in favor of secession. Independence was attained on 9 July 2011.
Location:
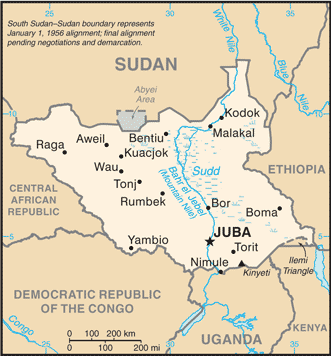
Location: East-Central Africa; south of Sudan, north of Uganda and Kenya, west
of Ethiopia.
Area: Total: 644,329 sq km, water: 129,810 sq km, land: 2.376 million sq
km.
Area - comparative: Slightly smaller than Texas.
Land boundaries: Total: 5,413 km, border countries: Central African Republic
989 km, Democratic Republic of the Congo 639 km, Ethiopia 934 km, Kenya 232 km,
Sudan 2,184 km, Uganda 435 km. Coastline: None.
Climate and Terrain:
Climate: hot with seasonal rainfall influenced by the annual shift of the
Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone; rainfall is heaviest in the upland areas of
the south and diminishes to the north.
Terrain: Terrain gradually rises from plains in the north and center to
southern highlands along the border with Uganda and Kenya.
Natural resources: Hydropower, fertile agricultural land, gold, diamonds,
petroleum, hardwoods, limestone, iron ore, copper, chromium ore, zinc,
tungsten, mica, silver.
People:
Population: 10,625,176.
Ethnic groups: Dinka, Kakwa, Bari, Azande, Shilluk, Kuku, Murle, Mandari,
Didinga, Ndogo, Bviri, Lndi, Anuak, Bongo, Lango, Dungotona, Achol.
Religions: Animist, Christian.
Languages: English (official), Arabic (includes Juba and Sudanese variants)
(official), regional languages include Dinka, Nuer, Bari, Zande, Shilluk.
Government:
Government type: Republic.
Capital: Juba.
Independence: Independence was attained on 9 July 2011.
Economy overview:
Industry and infrastructure in landlocked South Sudan are severely
underdeveloped and poverty is widespread, following several decades of civil
war with the north. Subsistence agriculture provides a living for the vast
majority of the population. Property rights are tentative and price signals are
missing because markets are not well organized. South Sudan has little
infrastructure - just 60 km of paved roads. Electricity is produced mostly by
costly diesel generators and running water is scarce. The government spends
large sums of money to maintain a large army; delays in paying salaries have
resulted in riots by unruly soldiers. Ethnic conflicts have resulted in a large
number of civilian deaths and displacement. South Sudan depends largely on
imports of goods, services, and capital from the north. Despite these
disadvantages, South Sudan does have abundant natural resources.
Statistics:
Television TV is controlled by the government; several private FM stations are
operational in South Sudan; some foreign radio broadcasts are available.
Railways: Est. 236 km; note - rail system reported to be in disrepair.
Highways: Est. 7,000 km; note - very little of the road network is paved and
much of it is in disrepair (2010).
Airports - with paved runways: 2, with unpaved runways: 22.
Return to Visiting Locations
|