|
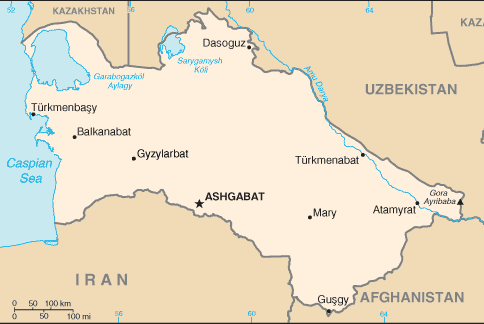
Turkmenistan
out.
Background:
Annexed by Russia between 1865 and 1885, Turkmenistan became a Soviet republic
in 1925. It achieved its independence upon the dissolution of the USSR in 1991.
President NIYAZOV retains absolute control over the country and opposition is
not tolerated. Extensive hydrocarbon/natural gas reserves could prove a boon to
this underdeveloped country if extraction and delivery projects can be worked
|
Climate and Terrain:
Climate: Subtropical desert.
Terrain: Flat-to-rolling sandy desert with dunes rising to mountains in the
south; low mountains along border with Iran; borders Caspian Sea in west.
Natural resources: Petroleum, natural gas, coal, sulfur, salt.
|
|
|
Economy overview:
Turkmenistan is largely desert country with intensive agriculture in irrigated
oases and large gas and oil resources. One-half of its irrigated land is
planted in cotton, making it the world's tenth-largest producer. With an
authoritarian ex-Communist regime in power and a tribally based social
structure, Turkmenistan has taken a cautious approach to economic reform,
hoping to use gas and cotton sales to sustain its inefficient economy.
Privatization goals remain limited. In 1998-2003, Turkmenistan suffered from
the continued lack of adequate export routes for natural gas and from
obligations on extensive short-term external debt. At the same time, however,
total exports rose by 38% in 2003, largely because of higher international oil
and gas prices.
|
|